
Managing Flammable Refrigerants: Reducing the Risk
Thirty years ago, researchers noticed that our upper atmosphere was getting thinner. This part is known as the ozone layer, where the mass of protective gases is located. It traps most of the ultraviolet radiation from the sun. It also reduces the amount of UV light that reaches the Earth’s surface by 98%. So how do flammable refrigerants come into play? Read on!
The depleted ozone layers are alarming because of their importance to human health. It also prevents radiation damage to plants, animals, and materials. Unprotected radiation causes skin cancer, eye cataracts, and other health ailments.
Scientists linked the presence of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and other ozone-depleting substances (ODS) to the thinning ozone layer. These synthetic chemicals are everywhere, particularly in refrigerants and fire extinguishers. It is also found in solvents, aerosol cans, foams, and soil fumigants.
The Kigali Amendment
Last January 1, 2019, 65 countries agreed to reduce the manufacture and use of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and potent greenhouse gases (GHGs). This was the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer. The “controlled substances” covered by the protocol also include hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, methyl bromide, methyl chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride.
All participating nations are required to reduce their use of HFCs, phasing them out by 2030. They are to substitute these substances with green alternatives to limit global warming by at least 0.4°C this century. This means the manufacture of refrigerants is regulated, especially those used in the foodservice industry. This concern also includes refrigerant disposal. As of the present, the more popular alternatives are flammable refrigerants and hydrocarbon (R290) refrigerants.
What are Flammable Refrigerants?
Refrigerants are substances used by air conditioning and refrigerating equipment that removes heat to cool objects. In an attempt to comply with the Kigali Amendment, the search was on for more compliant refrigerants. An increasing number of these flammable refrigerants were discovered over the years. It was noticed, however, that as the global warming potential (GWP) of a refrigerant decreases, the flammability increases.
Nevertheless, compared to the previous refrigerants, flammable refrigerants are the more eco-friendly option. Flammable refrigerants have a very low global warming potential (GWP), zero ozone depletion potential, are inexpensive, and are widely available. Although flammable, these flammable refrigerants are now used in refrigerators because of their high quality of energy efficiency. Minimizing the risk of explosions is achieved by sealing these toxic substances following standard regulations.
Here’s an article about the 3 Tube Sealing Applications for Air-conditioning and Refrigeration, learn how each application works depending on the needs.
How to Manage Flammable Refrigerants Risk?
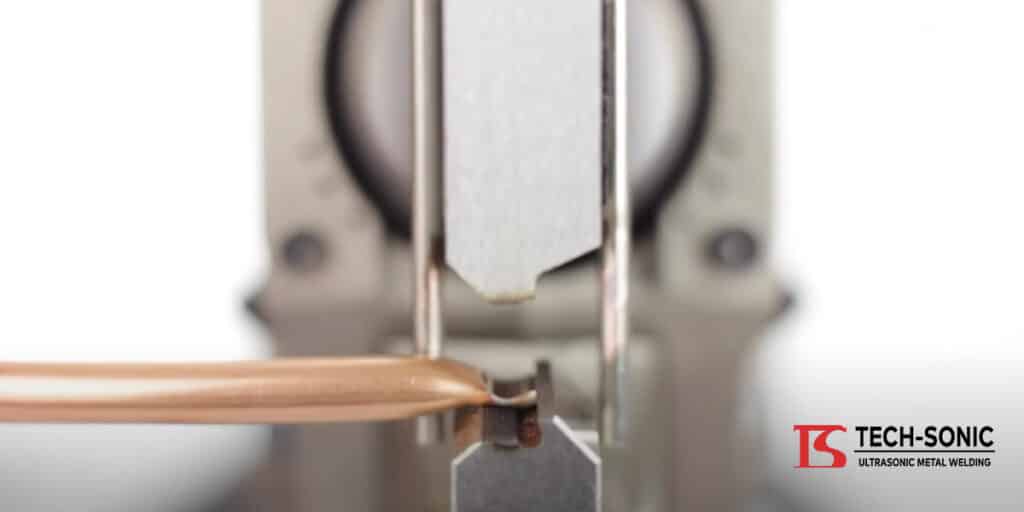
Although flammable refrigerants are hazardous, they can still be handled safely. A crucial step in ensuring safety in flammable refrigerants is tight sealing during the manufacturing process. The designed equipment used should handle these flammable refrigerants securely.
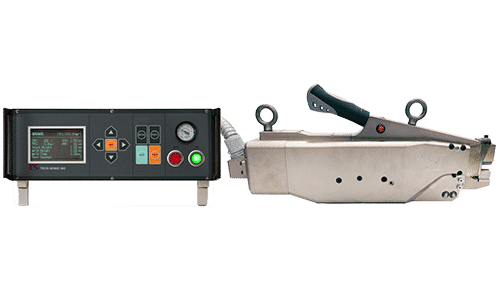
One of the approved machines to work with these flammable refrigerants is the US-3620TS-EX Ultrasonic Tube Sealer. This is TECH-SONIC’s explosion-proof ultrasonic tube sealer and it is compatible with hydrocarbons, hydrofluorocarbons, isobutene, and ammonia refrigerant alternatives. This model is used in applications for refrigerator manufacturers and HVAC manufacturers related to the EPA-Mandated HCFC phase-out and the Clean Air Act.
Ultrasonic welding is used instead of the traditional brazing methods that are not compatible with flammable gas. Hence, the US-3620TS-EX Ultrasonic Tube Sealer is recommended to safely seal the charged copper tubes used to store flammable refrigerants. The machine’s safety purge system also removes trapped gas from the weld actuator. This process begins before electric startup and remains active while powered up. This results in the elimination of any unsafe gas accumulation.
Facility supervisors should ensure the safety of their building, especially its occupants. In hospitals, administrators must protect their generally fragile patients. They should think of the often ignored risks of toxic and flammable refrigerants. TECH-SONIC’s US-3620TS-EX Ultrasonic Tube Sealer is Explosion-Proof Certified for operation with flammable HC alternatives. These certifications include Ex-Zone 2, Class 1, and Division 2 Certification, assuring a more secure solution in complying with the phase-out of ODS.
Featured Products

Ultrasonic Tube Sealer (Explosion Proof)
US-3620TS-EX

Ultrasonic Tube Sealer
US-3620TS
Ultrasonic Tube Sealer (Economy)
Falcon-KN
